To avoid running out of stock, retailers need to constantly replenish their inventory. That’s where wholesalers come in.
The difference between wholesale vs. retail is that retailers sell directly to consumers, whereas wholesalers sell to those retailers. Many retailers get their products from wholesalers, who play the crucial role of bridging the gap between manufacturers and retailers.
Wholesalers are an indispensable part of the supply chain, with the global wholesale market estimated to reach $68 trillion by 2033. Retailers, on the other hand, contribute approximately $3.9 trillion to the U.S. economy each year. Retail also accounts for more than 15.7 million jobs in the U.S.
But which is better for your business: wholesale or retail? Learn about their key differences, the pros and cons of each, and how to choose the right model for you.
What is wholesale?
Wholesaling is a distribution model where businesses buy items in bulk from manufacturers or distributors and sell them to other companies. Wholesalers can acquire products cheaply because they only purchase in large quantities. Essentially, wholesalers are the intermediary between manufacturers and retailers.

There are many benefits and challenges of wholesale. Here’s an overview.
| Pros and cons of wholesale | |
| Pros | Cons |
| Discounted rates for bulk purchases | Competitive landscape |
| Efficient distribution | Little control over branding |
| Better opportunity for growth | High initial costs with required bulk buying |
| Emphasis on partnerships | Requires a lot of storage space |
| Consistent revenue because of repeat buyers | Risk of cash flow issues because buyers often pay with credit |
What is retail?
Retailers sell their products directly to the customer after buying them from a wholesaler, the manufacturer, or producing them themselves. Retailers are required to have a thorough understanding of the marketplace and customer trends to keep up with demand. They must also have specific retail inventory management systems in place.

Here are some advantages and disadvantages of retail.
| Pros and cons of retail | |
| Pros | Cons |
| Building customer relationships | Lower value per sale |
| Potential for higher profits | Competitive landscape |
| High level of control over brand identity | Higher overhead costs |
| Wide range of operation options (online, over the phone, in-person, etc.) | More to manage compared to wholesale |
What's the difference between wholesale and retail?
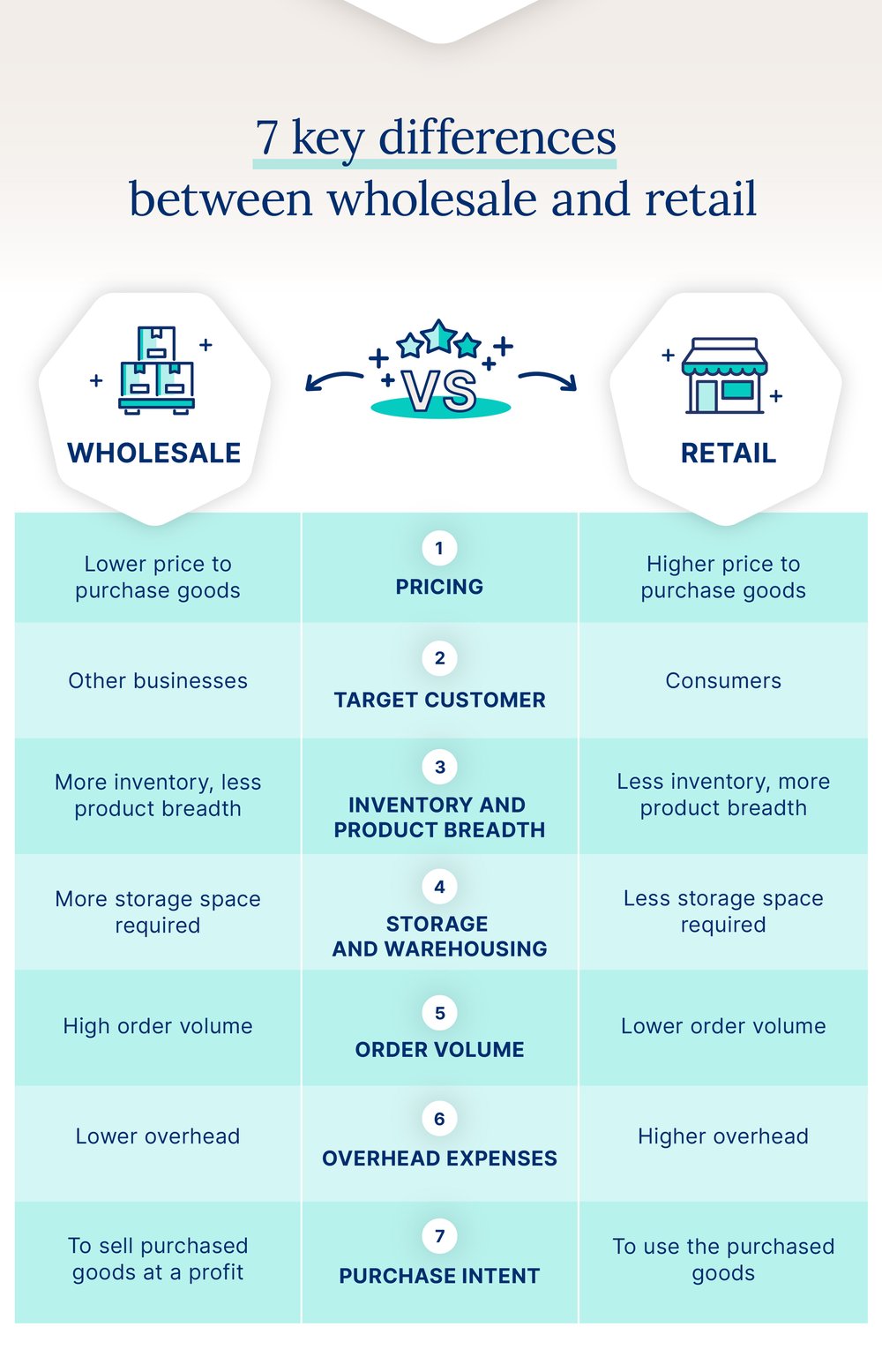
Although wholesalers and retailers are very closely related and perform similar functions, they are different from each other. The main difference between wholesale and retail is that retailers sell directly to the end customer, whereas wholesalers sell to retailers. Here are seven additional key differences to consider:
- Pricing: Wholesale price tends to be lower than retail price, as items are bought in large quantities to be sold at a profit for retail.
- Target customer: Wholesalers are generally business-to-business sellers (B2B), whereas retailers are usually business-to-consumer (B2C).
- Inventory and product breadth: Wholesalers have less product variety but maintain those products in higher volume. Retailers generally have less inventory but carry a larger variety of products.
- Storage and warehousing: Retailers have more limited storage options than wholesalers, which generally require a large warehouse space. The type of warehouse needed will depend on the specific products.
- Order volume: Wholesalers purchase large quantities from manufacturers, whereas retailers purchase smaller amounts from wholesalers.
- Overhead expenses: Retailers will have higher overhead expenses than wholesalers for things like marketing and customer experience.
- Purchase intent: Individuals who purchase from wholesalers resell those items at a higher price to their customers. Conversely, individuals who buy from retailers plan to use those items rather than sell them to someone else. Retailers who purchase from wholesalers are not consumers themselves; instead, they resell to consumers.
Types of wholesalers
From classic merchants to discount wholesalers, there are many different types of wholesale businesses. Each type serves unique roles in the supply chain, meeting specific market demands. Here are some of the most common types of wholesalers.
- Merchant: These wholesalers have a large inventory of products that they buy and then sell to retailers in smaller orders at an increased price to make a profit.
- Online: Online wholesalers sell all their products in bulk online.
- Sales and distribution: The manufacturer acts as its own wholesaler, selling products directly to other wholesalers or retailers.
- Discount: These wholesalers sell goods that are discontinued, returned, or on liquidation at an extreme discount.
- Brokers: Although not technically wholesalers themselves, brokers arrange for deals between wholesalers and retailers, collecting commissions and fees for sales.
Types of retailers
There is an extensive range of retailers, including grocery stores and online retailers like Amazon. Every kind of retailer aims to meet different consumer demands, from essential needs like food to niche interests. Here are some of the most common types of retailers.
- Online: Online, or e-commerce, stores sell their products online, as the name suggests. Many retailers have a combination of online and brick-and-mortar stores.
- Department store: This type of retailer sells a variety of products, including home goods, clothing, jewelry, and more.
- Grocer: Grocery stores sell food products and other home goods such as cleaning supplies, stationery, and beauty products.
- Convenience: Convenience stores, also called corner stores, sell basic items such as snacks, toiletries, and drinks, often at an increased price compared to other grocery stores.
- Discount: These retailers sell a wide range of inventory at reduced costs. Kmart and Aldi are some examples.
- Specialty: This type of store sells a small range of specialty items, such as a pet supply store or florist.

Retail vs. wholesale: Which is right for your business?
Choosing the right method of selling products is dependent on many factors. From what your goals are to the ideal customer, here are some things to consider.
Considerations for wholesalers
Wholesale may be a good option for you if you’re interested in:
- Increased brand awareness: As a wholesaler, your products can end up in any number of categories and stores, having a wider reach. Retailers, however, have more control over their brand identity.
- Growth opportunities: Wholesalers are not limited geographically and can expand their marketplace internationally.
- Less marketing: With a B2B model focused on building partnerships with other businesses, less marketing is required.
- Managing bulk orders: This includes having inventory management systems in place as well as storage available for goods.
Considerations for retailers
Retail may be a good option for you if you’re interested in:
- Consumer demand: Successful retailers have a thorough understanding of market trends and customer trends, ordering products that will sell well and meet their customers’ expectations.
- Close client relationships: Being a retailer means working directly with the end customer to meet their needs.
- Strategic marketing: Selling directly to customers requires a strong marketing strategy.
- A high level of control: Retailers control their pricing models, brand identity, market strategies, target markets, and more.
Considerations for manufacturers
For manufacturers deciding if they’ll sell products to a wholesaler or retailer, there are several factors to consider. Both have their benefits and drawbacks. Here are some considerations:
- Order volume: Wholesale items are sold in bulk, allowing for the movement of a large amount of inventory at once. Retail items are sold in smaller quantities compared to wholesale.
- Buyer relationships: Both wholesale and retail rely on close buyer relationships with whomever they’re getting their products from. Relationship building is an essential skill for success for either.
- Target customer: Wholesalers and retailers are not the end customer for the product. However, wholesalers usually sell their product to a retailer, who then sells it to the end customer. Selling directly to the retailer cuts out the middleman.
- Pricing: Wholesalers receive discounts on bulk orders, while retailers may be limited in how much they can spend and store.
Manage wholesale and retail easily with Cin7
When deciding between wholesale vs. retail for your business, there’s a lot to consider. The most important factor is understanding your target market and implementing inventory management solutions to ensure you can keep up with demand.
Learn more about how Cin7 can help you manage your inventory.
FAQ
What is the wholesale vs. retail price?
Wholesalers buy products in bulk directly from the manufacturer at a discounted price. Buying products from wholesalers is therefore less expensive than retail. Retail price is calculated by adding a markup to the cost of goods.
What is the difference between a retailer and a wholesaler?
Retailers buy their products from wholesalers or manufacturers and sell them at a markup to the consumer. Wholesalers do not sell directly to the consumer but buy products from the manufacturer to then sell to retailers as an intermediary.
What is an example of a wholesaler?
Alibaba is an online wholesaler based in China. They have a wide variety of products that they buy from various suppliers and then sell in bulk to retailers, who sell directly to consumers.
Is Walmart a wholesaler or a retailer?
Walmart is considered a discount retailer. They buy their products from various wholesalers and then sell them to customers.
Can a business be both a retailer and wholesaler?
Yes, many companies operate as both retailers and wholesalers. However, these operations are usually managed separately as they have different requirements. An example of this is a company like Apple that manufactures its products, distributes to retailers, and has its own retail operation.
More from the blog
View All Posts
Essential e-commerce technology trends to implement in 2024
Read More
How to Know What Platform or Channel is Right for Me
Read More




